A fault tree is an organised graphical representation of the conditions or other factors causing or contributing to the occurrence of a defined outcome, referred to as the “top event”.
Fault tree analysis is a deductive (top-down) method aimed at pinpointing the causes or combinations of causes that can lead to the defined undesirable outcome and which affect product performance, safety, economy, or other specified characteristics.
The Fault tree can also be constructed to provide a system reliability prediction model and allow trade-off studies in a design phase. It can be started early in the stages of a design and further developed in detail concurrently with design development. Typical applications include evaluation of Safety Integrity Levels (SIL).
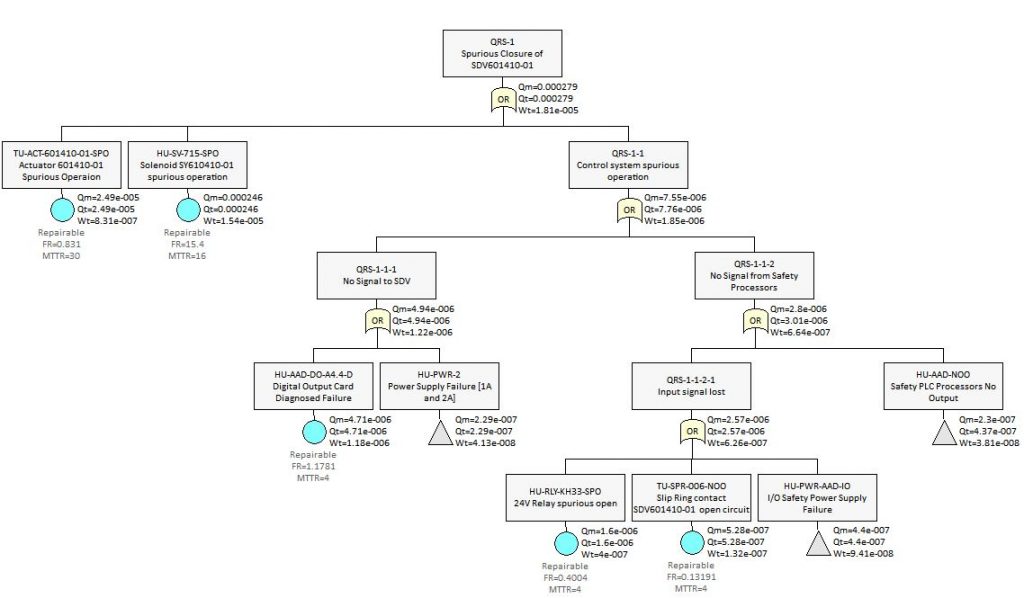
The Fault Tree is developed by identifying the ‘immediate and necessary’ events which give rise to the event described at the top event or intermediate ‘Gate’. If the event is one which can be completely described and allocated its own reliability parameters, it is referred to as a ‘Basic Event’. If more than one Basic Event is required to cause the event described, they are combined under a logic ‘Gate’. The process continues until only BasicThe Events are needed to fully describe an event.The input reliability and repair data is displayed beneath each Basic Event and the calculated reliability parameters are displayed next to each logic gate. Reliability parameters for a gate are derived from the identified ‘Minimal Cut Sets’
